A) Heart
1) Mechanism of heart beating :
- Heart beat simultancously and rhythmic to pump blood along blood vascular system

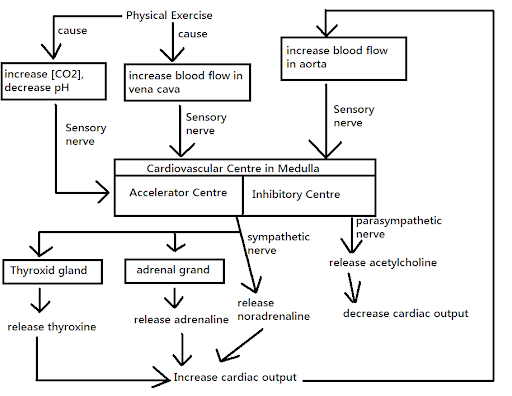
2) Nerves control of heartbeat :
3) Cardiac cycle :

* Blood flow from high pressure to low pressure
B) Blood Vessel :
Structural Adaptation of Blood Vessel :
1) Arteries :
- Thick Wall : Withstrand high blood pressure
- Thick elastic fibres : Recoil after the dilution, push blood further away
- Nerve supply : regulate the diameter of the arteries


2) Vein :
- Valve : prevent backflow
- Large lumen : reduce resistance
- Attached by skeletal muscle : force blood forward


3) Capillary :
- Protein channel : allow small molecule pass through
- Thin wall : rapid diffusion
- Small diameter : slow blood flow allow longer time to exchange
- Network of capillary : increase surface area
- Close to tissue : shorten the distance



C) Blood :
1) Oxygen dissociation curve :
 |
|
2) Bohr effect :
 |
(CO2 diffuse forms carbonic acid, carbonic acid dissoicate to liberate H+, H+ combine with haemoglobin to displace O2 ) |
3) Adaptation of organism :
For organism living in low oxygen tension atmosphere :
 |
|
For high metabolic organism :
 |
|
D) Lymph :
1) Mechanism of forming lymph :
- High blood pressure at the arteries end of capillary, due to (1)pumping action of heart and (2)high pressure of artery
- The high hydrostatic pressure exceeds the osmotic pressure in blood, which force all constituents of blood plasma except large protein out to the intercellular space through capillaries wall by filtration forming tissue fluid.
- Most of the tissue fluid is drawn back into capillary by osmosis due to high water potential of the tissue fluid at the intercellular space the rest of them is forced into the lymphatic vessel forming lymph.
2) Significant of lymph :
- Forming linkage between tissue fluid and blood vascular system
- Transport absorbed fat from lacteals
- lymph node (a) produce lymphocytes which produce antibody to neutrolize the effect of antigen, thus ,it is a part of immune system. (b) phagocyte engulf bacteria and foreign particle in lymph
沒有留言:
張貼留言