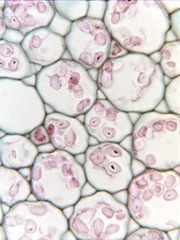
Cell types
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| -alive | -alive | -dead |
| -thin cell wall | -uneven thickening of cell wall, extra deposit of cellulose | -liginifed cell wall, empty lumen |
| -provide support when turgid | -mechanism support with elastivity | -strong mechanism support |
| -lots of intercellular space -may contain chlorophyll -unspecilized | -can growth without limiting other cell | -unable to elongate when mature |
 |  |  |
Stem anatomy

Root anatomy
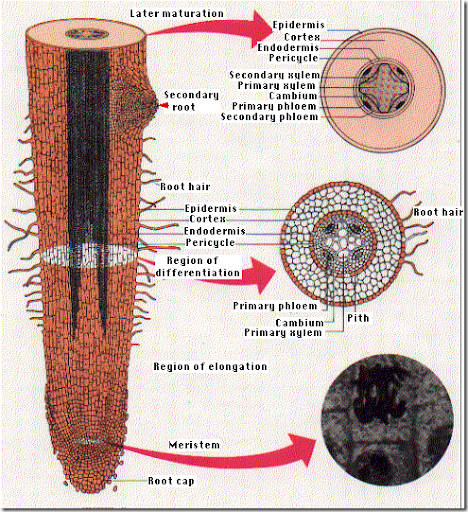
The comparesion between the means of support of aquatic plant and terrestrial plant
| Terrestrial plant | Aquatic plant | |
| Collenchyma | V | X |
| Sclerenchyma | V | X |
| Air space | X | V |
| xylem | well developed to support, highlt lignified | poor developed, not to support |
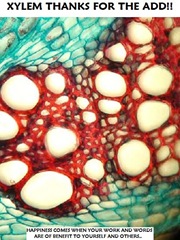
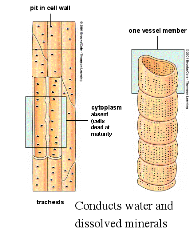
Structural adaptation of xylem tissue
|     |
Structural adaptation of phloem tissue


沒有留言:
張貼留言